The U.S. National Security Agency (NSA) on Friday said DNS over HTTPS (DoH) — if configured appropriately in enterprise environments — can help prevent “numerous” initial access, command-and-control, and exfiltration techniques used by threat actors.
“DNS over Hypertext Transfer Protocol over Transport Layer Security (HTTPS), often referred to as DNS over HTTPS (DoH), encrypts DNS requests by using HTTPS to provide privacy, integrity, and ‘last mile’ source authentication with a client’s DNS resolver,” according to the NSA’s new guidance.
Proposed in 2018, DoH is a protocol for performing remote Domain Name System resolution via the HTTPS protocol.
One of the major shortcomings with current DNS lookups is that even when someone visits a site that uses HTTPS, the DNS query and its response is sent over an unencrypted connection, thus allowing third-party eavesdropping on the network to track every website a user is visiting.
Even worse, the setup is ripe for carrying out man-in-the-middle (MiTM) attacks simply by changing the DNS responses to redirect unsuspecting visitors to a malware-laced site of the adversary’s choice.
Thus by using HTTPS to encrypt the data between the DoH client and the DoH-based DNS resolver, DoH aims to increase user privacy and security by preventing eavesdropping and manipulation of DNS data by MiTM attacks.
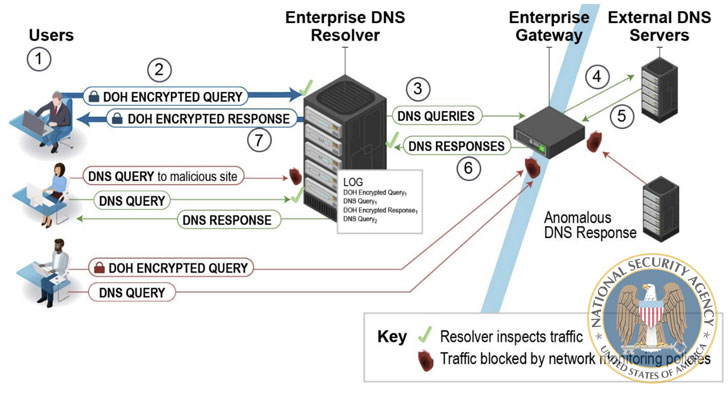
To that effect, the NSA recommends using only designated enterprise DNS resolvers to achieve the desired cybersecurity defense, while noting that such resolvers will be bypassed completely when a client has DoH enabled and is configured to use a DoH resolver not designated by the enterprise.
The gateway, which is used to forward the query to external authoritative DNS servers in the event the enterprise DNS resolver does not have the DNS response cached, should be designed to block DNS, DoH, and DNS over TLS (DoT) requests to external resolvers and DNS servers that are not from the enterprise resolver, the agency added.
Although DoH protects DNS transactions from unauthorized modification, the NSA cautioned of a “false sense of security.”
“DoH does not guarantee protection from cyber threat actors and their ability to see where a client is going on the web,” it said. “DoH is specifically designed to encrypt only the DNS transaction between the client and resolver, not any other traffic that happens after the query is satisfied.”
“Enterprises that allow DoH without a strategic and thorough approach can end up interfering with network monitoring tools, preventing them from detecting malicious threat activity inside the network, and allowing cyber threat actors and malware to bypass the designated enterprise DNS resolvers.”
What’s more, the encryption does nothing to prevent the DNS provider from seeing both the lookup requests as well as the IP address of the client making them, effectively undermining privacy protections and making it possible for a DNS provider to create detailed profiles based on users’ browsing habits.
Oblivious DNS-over-HTTPS (ODoH), announced last month by engineers at Apple, Cloudflare, and Fastly, aims to address this issue. It prevents the DoH resolver from knowing which client requested what domain names bypassing all requests via a proxy that separates the IP addresses from the queries, “so that no single entity can see both at the same time.”
Put differently, this means the proxy does not know the contents of queries and responses, and the resolver does not know the IP addresses of the clients.
Secondly, the use of DoH also doesn’t negate the possibility that resolvers that communicate with malicious servers upstream could still be susceptible to DNS cache poisoning.
“DNSSEC should be used to protect the upstream responses, but the DoH resolver may not validate DNSSEC,” the NSA said. “Enterprises that do not realize which parts of the DNS process are vulnerable could fall into a false sense of security.”
Found this article interesting? Follow THN on Facebook, Twitter and LinkedIn to read more exclusive content we post.
Read More
The post NSA Suggests Enterprises Use ‘Designated’ DNS-over-HTTPS’ Resolvers appeared first on Malware Devil.
https://malwaredevil.com/2021/01/16/nsa-suggests-enterprises-use-designated-dns-over-https-resolvers/?utm_source=rss&utm_medium=rss&utm_campaign=nsa-suggests-enterprises-use-designated-dns-over-https-resolvers